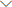There are two main types of DC motors: brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors.
1. Brushed DC motor
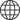
DC motors are known for their good starting performance, speed regulation performance and other advantages. Among them, brushed DC motors belonging to DC motors use mechanical commutators to make the driving method simple. The schematic diagram of the model is shown in Figure 1.2.
The motor is mainly composed of a stator made of permanent magnet materials, a rotor (armature) with coil windings, a commutator, and brushes. As long as a certain amount of DC current is applied to both ends of the brushes A and B, the commutator of the motor will automatically change the direction of the magnetic field of the motor rotor, so that the rotor of the DC motor will continue to run.
It can be seen from these that the commutator and brushes play an important role in the DC motor. Although it can simplify the structure of the motor controller, it has certain shortcomings:
Z The structure is relatively complicated, which increases the manufacturing cost;
Z is easily affected by the environment (such as dust, etc.), which reduces the reliability of the work;
Z Sparks will be generated when commutation, which limits the scope of use;
Z It is easy to be damaged, which increases the maintenance cost and so on.
2. Brushless DC motor
The birth of the brushless DC motor (Brushless Direct Current Motor, BLDCM) overcomes the congenital defects of the brushed DC motor, and replaces the mechanical commutator with an electronic commutator, so the brushless DC motor has both a good adjustment of the DC motor. It also has the advantages of simple structure, no reversing spark, reliable operation and easy maintenance.
The brushless DC motor model shown in Figure 1.3 is a model converted from Figure 1.2. It is mainly composed of a rotor made of permanent magnet materials, a stator with coil windings and a position sensor (optional). It can be seen that it has a lot in common with a DC motor. The structure of the stator and the rotor are similar (the original stator becomes the rotor, and the rotor becomes the stator), and the winding connections are basically the same. However, they have an obvious difference in structure: the brushless DC motor does not have the commutator and brushes in the DC motor, instead it is a position sensor. In this way, the motor structure is relatively simple, which reduces the cost of manufacturing and maintenance of the motor, but the brushless DC motor cannot automatically commutate (phase). The sacrifice is the increase in the cost of the motor controller (such as the same three-phase DC motor, there are The drive bridge of the brushed DC motor needs 4 power tubes, while the drive bridge of the brushless DC motor needs 6 power tubes).